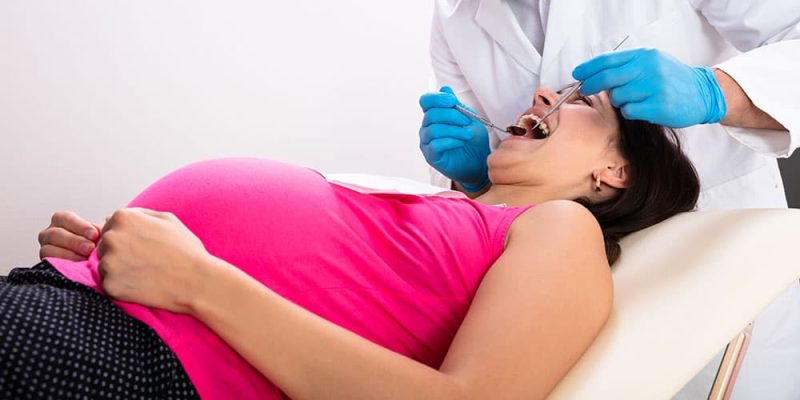
Pregnancy is a time of significant physical and emotional change, and maintaining good oral health is crucial for the health and well-being of both mother and baby. However, hormonal fluctuations and changes in oral health habits can increase the risk of gingivitis, a mild gum disease. If you’re an expectant mother, it’s essential to work with a qualified dentist in Glen Carbon who understands the unique oral health needs of pregnant women. By prioritizing your oral health and seeking regular care from a trusted dentist, you can reduce your risk of gingivitis and other oral health complications, ensuring a healthy and happy pregnancy.
Exploring The Link Between Pregnancy and Gingivitis
Pregnancy hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a significant role in the development of gingivitis. These hormones can cause changes in the gums, making them more susceptible to inflammation and infection.
Additionally, pregnancy can lead to changes in oral health habits, such as:
- Increased sugar cravings: Consuming high-sugar foods and drinks can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Morning sickness: Frequent vomiting can lead to acid erosion of the teeth and gums.
- Fatigue: Exhaustion can make it difficult to maintain good oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing.
Understanding The Risks Associated with Untreated Gingivitis During Pregnancy
Untreated gingivitis can lead to more severe gum disease, which has been linked to various pregnancy complications, including:
- Preterm labor: Research suggests that women with gum disease are more likely to experience preterm labor.
- Low birth weight: Babies born to mothers with gum disease are at a higher risk of being born with low birth weight.
- Pregnancy-induced hypertension: Gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension.
- Diabetes: Women with gum disease are more likely to develop gestational diabetes.
Managing Gingivitis During Pregnancy
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you manage gingivitis during pregnancy:
Step 1: Practice Good Oral Hygiene Habits
- Brush regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily: Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash: Rinsing with an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and inflammation in the mouth.
Step 2: Visit Your Dentist Regularly
- Schedule regular check-ups: Visit your dentist every 6 months for a routine check-up and cleaning.
- Inform your dentist about your pregnancy: Let your dentist know about your pregnancy so they can take necessary precautions and provide personalized care.
- Follow your dentist’s recommendations: Your dentist may recommend more frequent cleanings or other treatments to help manage gingivitis.
Step 3: Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid sugary and acidic foods: Limit your consumption of sugary and acidic foods, which can contribute to tooth decay and gingivitis.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help keep your mouth moist and wash away bacteria.
Step 4: Manage Stress and Get Enough Rest
- Practice stress-reducing techniques: Stress can exacerbate gingivitis, so try stress-reducing techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help your body and mouth recover from the day.
Step 5: Consider Professional Dental Cleaning
- Deep cleaning: If you have gingivitis, your dentist may recommend a deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Antibacterial treatments: Your dentist may also recommend antibacterial treatments, such as antibacterial mouthwashes or gels, to help reduce bacteria and inflammation in the mouth.
Remember, a healthy smile is just as important as a healthy body during pregnancy.






Comments