Gum grafting, or gum transplantation, is a surgical procedure offered by a dentist in San Jose, CA. It involves transferring healthy gum tissue from one part of the mouth to another. This procedure is used to cover exposed roots, restore receding gums, and promote new tissue growth. Let’s explore more about this common periodontal procedure.
Why is gum grafting performed?
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure that involves transferring healthy gum tissue to an area where the gum has receded or been damaged. Here are some reasons why gum grafting may be necessary:
- Exposed roots: Gum recession can cause roots to become exposed, leading to sensitivity and increased risk of decay.
- Receding gums: Gum tissue can recede due to periodontal disease, aggressive brushing, or genetics.
- Gum disease: Advanced gum disease can cause significant gum loss.
- Tooth sensitivity: Exposed roots can cause sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
- Aesthetic concerns: Receding gums can affect the appearance of the smile.
- Bone loss: Gum recession can lead to bone loss, which can affect the stability of teeth.
- Tooth loss: If left untreated, gum recession can lead to tooth loss.
- Root decay: Exposed roots can decay, leading to cavities and potentially affecting the surrounding teeth.
- Gingivitis: Gum grafting can help treat gingivitis by covering exposed roots and restoring gum tissue.
- Improved oral health: Gum grafting can improve oral health by restoring gum tissue and reducing the risk of decay and disease.
It’s important to consult a dentist or periodontist if you’re experiencing any of these issues to determine if gum grafting is the right solution for you.
What are the types of gum grafting?
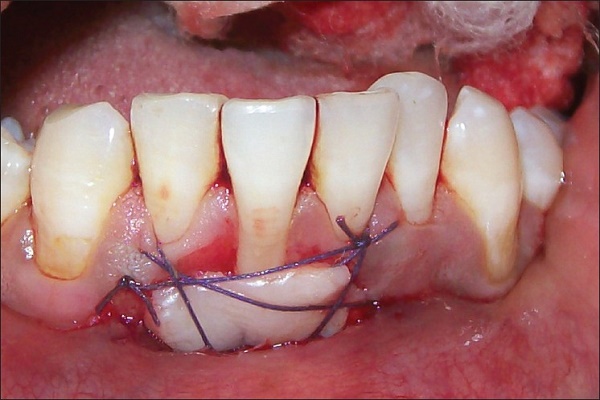
There are three main types of gum grafting procedures:
Connective tissue graft:
– Most common type
– Tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth (palate)
– Used to cover exposed roots and restore gum tissue
Free gingival graft:
– Tissue is taken from the palate
– Used to cover exposed roots and restore gum tissue
– More complex than connective tissue graft
Pedicle graft:
– Tissue is taken from nearby gum tissue
– Used to cover exposed roots and restore gum tissue
– Less common than connective tissue graft
Additionally, there are two other types of gum grafting procedures:
Allograft:
– Uses donated human tissue
– Used for larger defects or when the patient’s tissue is not available
Xenograft:
– Uses animal-derived tissue (usually porcine)
– Used for larger defects or when the patient’s tissue is not available
It’s important to consult a dentist or periodontist to determine the most appropriate type of gum grafting procedure for your specific needs.
How is gum grafting performed?
The procedure for gum grafting typically involves the following steps:
- Initial consultation: Consult with a dentist or periodontist to determine if gum grafting is necessary.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used to numb the area to minimize discomfort.
- Tissue harvesting: Healthy gum tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth (palate) or another area of the mouth.
- Grafting: The harvested tissue is grafted to the recipient site, covering exposed roots or restoring gum tissue.
- Suturing: The graft is secured with sutures to hold it in place.
- Recovery: The area is allowed to heal, which may take a few weeks.
- Follow-up: Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing and remove sutures.
The procedure may vary depending on the type of graft and individual needs. Your dentist or periodontist will provide personalized instructions and guidance throughout the process.
- Aftercare:
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities
- Eat soft foods
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Keep the area clean
- Follow post-operative instructions
Conclusion
Gum grafting is an effective procedure for restoring receding gums and promoting new tissue growth. While it may seem intimidating, the procedure is relatively straightforward and can have a significant impact on oral health and aesthetics. Consult with a dentist or periodontist to determine if gum grafting is right for you.







Comments